A project coordinated by the University of Oviedo has obtained around 1.5 M € of European Union funding in the LIFE Programme in Environment and Resource Efficiency. The academic institution initiative regarding Circular Economy European strategy has been called “SUBproducts4LIFE, Innovative circular economy concepts by reusing industrial subproducts and waste”.
The project, coordinated by the University of Oviedo, has a budget of almost 1.5 M €. It will start the recovery of La Soterraña mine, located in the valley of Muñón (Municipalty of Lena).
SUBproducts4LIFE will set the basis for the remediation of La Soterraña exploitation , located in the Muñón valley, council of Lena. La Soterraña was active since 1950 until 1974 and was affected by heavy metals contamination like mercury and arsenic. More than 40 years after its closure, this will be the first project aiming its partial remediation. Actions in El Terronal site, council of Mieres will also be carried out.
The partnership is formed by big companies like Grupo Masaveu Industria (Edersa) and EDP and SMEs like Biosfera, Global Services and Tecnología del Medio Ambiente y Minería. The Lena Municipalty will colaborate as co-financer and the Government of the Principality of Asturias is involved by the Asturian Institute for the Prevention of Occupational Risks.
SUBproducts4LIFE is commited to the industrial subproducts and waste reuse. It will be used to rehabilitate contaminated soils and degraded industrial areas.
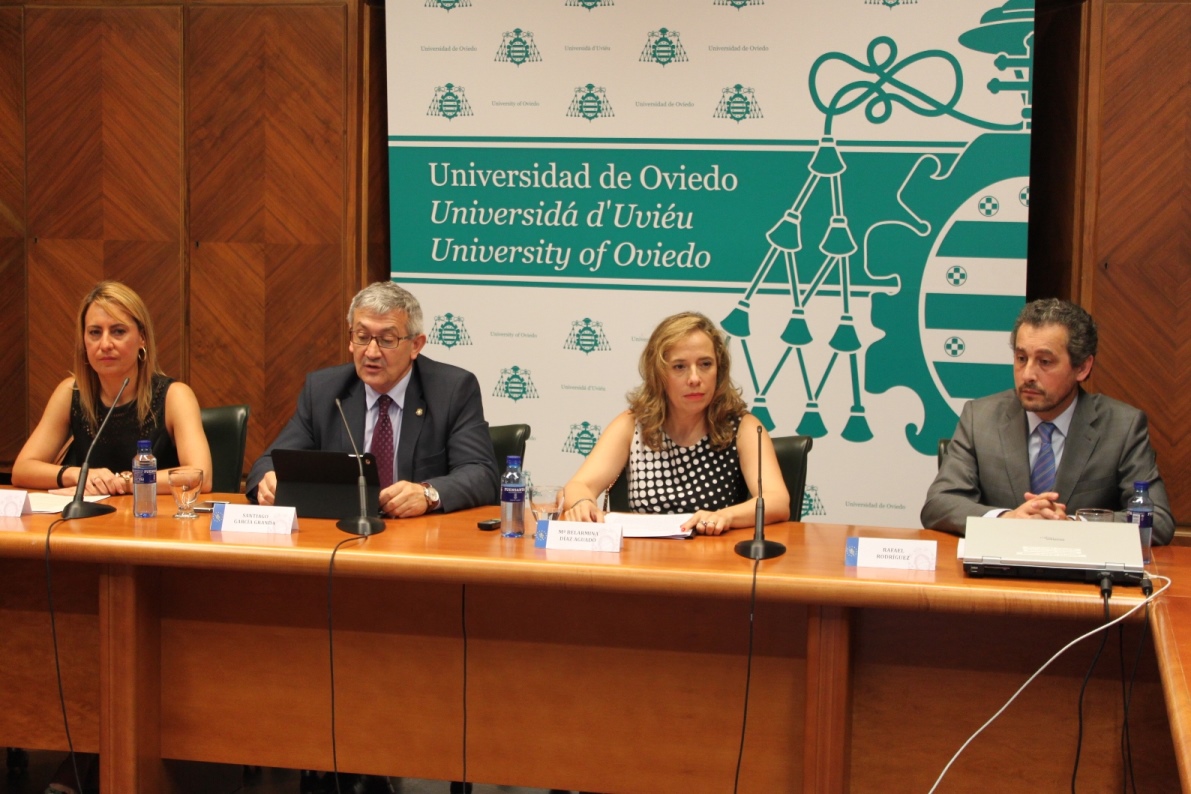
The Rector, Santiago García Granda, presented SUBproducts4LIFE in a press conference alongside the Director-General of Mining and Energy of the Principality of Asturias, Mª Belarmina Díaz Aguado; the Lena mayoress, Gemma Álvarez; and the Principal Investigator of the project, Rafael Rodríguez Díez, from University of Oviedo.
The technical explanation of the project was done by Rafael Rodríguez, Principal Investigator. He pointed that SUBproducts4LIFE will work in two main directions: “In the first place, the waste treatment to improve its situation. In the other side, the water treatment, to avoid the rain water contamination”. Between 15,000 and 20,000 tn of subproducts (coal ashes and gypsum) will be used.